LiDAR in Civil Engineering
What is LiDAR?
The acronym of LiDAR is Light Detection and Ranging, which is a form of remote sensing method used to examine the surface surrounding it. It is the surveying method that calculates the distance of an object by illuminating the object with the senor. The working is much similar to a radar sensor but instead of sending radio waves, it emits a pulse of infrared light and measures how long they take to come back after hitting nearby objects.
How do LiDAR works?
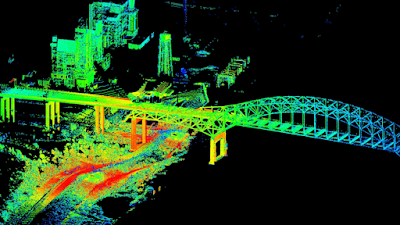
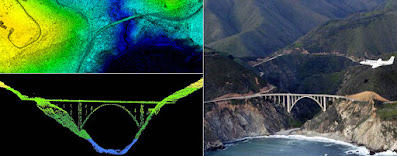
The sensor emits the infrared light millions of times in a second and then the readings are compiled and results into a so-called point cloud which you can say a 3-D image in real-time.
The working principle of LiDAR is really quite simple. The sensor generates a laser pulse train sent to the surface/object to measure the time and it takes to return to the source again.
Much accurate distance can be then calculated to the points on the ground and elevation can be determined along with the ground surface, buildings, and road ca be recorded.
I have seen a documentary in Discover-Plus where in Central America the tombs and pyramids which are unknown till now under the great forest of Central America, here LiDAR have been proved to be truly helpful for finding unknown sites of an ancient civilization.
LiDAR use in Civil Engineering?
There is the various application of LiDAR in Civil Engineering:
1. LiDAR in Surveying:
Using LiDAR in surveying can be classified as Topographic LiDAR Survey where Topographic data using an airborne method whereas in Hydrographic LiDAR Survey data is collected using ships and airborne mechanisms.
2. LiDAR in Geology:
In Geology a combination of airborne LiDAR and GPS is used as an evolved into an important tool for fault and measuring uplifts. This can also be used to find the glaciers, and generate significant use in advance Geology. It can help to find the changing slope and land break to find the soil pattern of any area.
3. LiDAR in Sewer and Manhole Maintenance:
LiDAR can collect data that can scan the area that is far and dangerous for a human to enter. The sensor can be mounted on a remote-operated vehicle and sent down in sewer to find a detailed survey of the interior system.
4. LiDAR in BIM:
This LiDAR can be used in work to find the plans of the project and help in various work such as scaling, checking the work, and correlating it with the system to check the design and maintain smooth working.
5. LiDAR in Tunnel Surveying:
As we saw that it is used for accurate and detailed measurement and analysis and assessment and modeling of the tunnel that is for railway or roadway. This can be done in the mountain, on land, and undersea.
6. LiDAR in Transportation Engineering:
LiDAR can be used in road planning, maintenance assessments, bridge construction with speed, accuracy, and flexibility. Once road data is collected, the quality model can be achieved quickly and with accurate results.
7. LiDAR in Mining & Quarries:
LiDAR in Mining and Quarries can be used to find volume measurements, mine mapping, tunnel construction with accuracy, flexibility, and safety. After getting the data, mining and quarry companies can see the need and available resources of the area.
Use and Future:
As far as I have seen LiDAR is most useful in Surveying in the Civil Engineering Industry. LiDAR surveying is used in the fields of construction, urban planning, and the topography of the region. As it collects data very fast and thus is superior to conventional forms of surveying.
Also as I told you that in Discovery Plus / NatGeo has a series, it is based on Archaeological Department.
https://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/news/00000161-4d54-d807-a9f3-4d5c18240000
To find new stuff in dense forest sites and unknown regions, LiDAR saves time as well as the efforts of the Archaeologists.
This method is most futuristic and helps many with the fast and accurate data collection and the 3-D view of the models.


Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You for visiting, if you have any questions please feel free to ask: